The Old Testament is a rich source of historical and religious narratives, filled with references to various regions and places that hold significant importance in understanding the sacred scriptures. From biblical cities to holy sites and ancient locations, these Old Testament places offer a glimpse into the cultural, historical, and religious context of the Bible.
Key Takeaways:
- Old Testament places encompass biblical cities, holy sites, and ancient locations.
- These regions serve as biblical landmarks, holding historical and religious significance.
- Exploring these sacred spots enhances our understanding of the narratives and history recorded in the Old Testament.
- Significant sites in the Old Testament include Canaan, Egypt, the Jordan River Valley, and the coastal regions.
- The Old Testament places provide insights into the cultural, historical, and religious context of the Bible.
Nations mentioned in the Bible
The Bible is a rich source of historical accounts and narratives, mentioning various nations that played pivotal roles in biblical history. These nations, scattered across different regions, have shaped the events and contexts recorded in the Old Testament. Let’s explore some of the significant nations mentioned in the Bible:
- The Ammonites: A nation known for their conflicts with the Israelites, particularly during the time of the Judges.
- The Amorites: A powerful people who inhabited Canaan and were conquered by the Israelites under Joshua’s leadership.
- Assyria: A mighty empire that eventually conquered the northern kingdom of Israel and exiled its inhabitants.
- Babylon: An ancient city and empire that played a major role in the downfall of the southern kingdom of Judah and the exile of its people.
- Canaan: The land promised to the Israelites as their inheritance, and later became the land of the twelve tribes of Israel.
- Edom: A nation descended from Esau, the twin brother of Jacob (Israel).
- Egypt: A significant nation in biblical history, which holds immense importance in the narratives of the Old Testament.
- Ethiopia: A nation mentioned as a distant land associated with Cush in the Bible.
- Greece: Though not as prominent as other nations in the Old Testament, Greece had occasional interactions with Israel.
- Israel: The nation chosen by God to be His people, with a rich history chronicled in the Bible.
- Italy: The mention of Italy in the Bible is primarily associated with the events surrounding the apostle Paul.
- Persia: The Persian Empire, which conquered Babylon and allowed the Israelites to return to their land and rebuild the temple.
- Syria: A nation that often interacted with Israel and had both friendly and adversarial relations throughout history.
These nations, with their unique roles and contributions, provide valuable insights into the historical and cultural tapestry of the Old Testament.
Historical Map
| Nation | Significance |
|---|---|
| Ammonites | Conflicts with Israel during the time of Judges |
| Amorites | Conquered by Israel under Joshua’s leadership |
| Assyria | Conquered Israel and exiled its inhabitants |
| Babylon | Conquered Judah and exiled its people |
| Canaan | Promised land and inheritance of Israel |
| Edom | Nation descended from Esau |
| Egypt | Significant role in biblical history and narratives |
| Ethiopia | Associated with Cush as a distant land |
| Greece | Occasional interactions with Israel |
| Israel | Chosen people with a rich history |
| Italy | Events surrounding the apostle Paul |
| Persia | Conquered Babylon and allowed Israel’s return |
| Syria | Interactions with Israel throughout history |
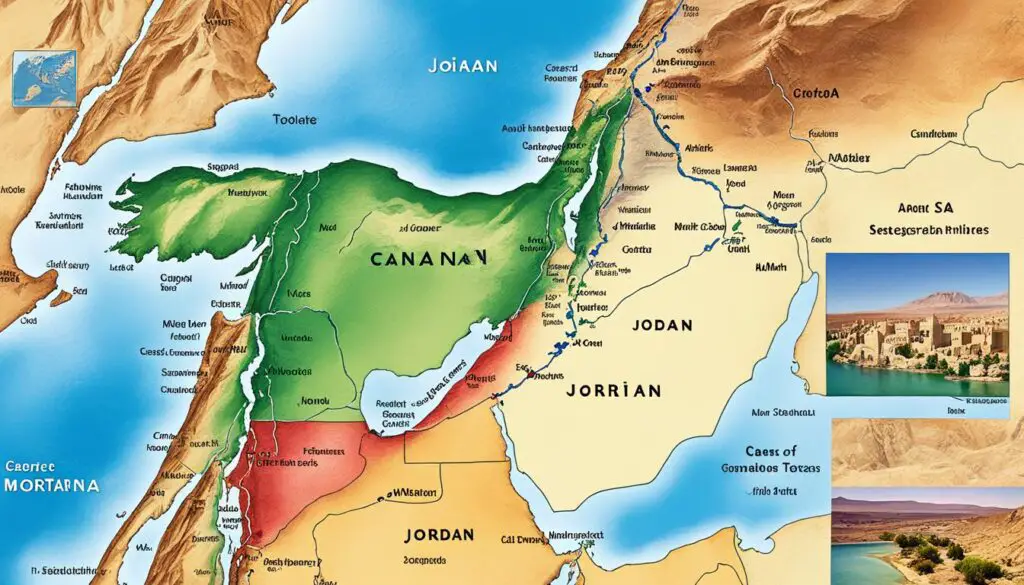
Geographical features of the Bible world
The Bible world was home to a diverse range of geographical features that shaped its history and significance. From ancient lands to sacred sites, let’s explore the remarkable landscapes of the Old Testament.
One of the main regions in the Bible world was Egypt. Known for its rich history and cultural heritage, Egypt played a significant role in the Old Testament. Notable locations like Goshen, the Nile River, and the cities of Memphis and Thebes are mentioned in biblical narratives.
The land of Canaan, also known as Palestine, holds immense biblical importance. This region was promised to the Israelites and became the land of the twelve tribes of Israel. Cities like Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Jericho, Hebron, and the Jordan River played crucial roles in the Old Testament stories, marking significant events and establishing religious and historical landmarks.
North and east of Palestine lay the territories that encompassed Syria, Assyria, and Babylon. These ancient locations were key players in the biblical narratives, influencing the events and interactions of the Israelites with neighboring nations.
| Geographical Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Fertile Crescent | A crescent-shaped land area spanning from Egypt through the Holy Land to Mesopotamia, hosting many ancient civilizations mentioned in the Bible. |
| Egypt | Ancient land of pyramids and pharaohs, associated with key events involving the Israelites, such as the Exodus and enslavement. |
| Canaan (Palestine) | The Promised Land for the Israelites, encompassing cities and landmarks of great religious and historical significance. |
| Syria | A region north of Palestine, mentioned in the Old Testament for its influence on the Israelites and connections with Assyria and Babylon. |
| Assyria | An ancient empire surrounding modern-day Iraq and Syria, impacting the Israelites and playing a role in biblical history. |
| Babylon | A significant city and empire in Mesopotamia, known for its conquest of the Kingdom of Judah and the subsequent exile of the Israelites. |
Summary
The geographical features of the Bible world provide a backdrop for the rich tapestry of stories and events recorded in the Old Testament. From the majestic Nile to the fertile lands of Canaan, these ancient locations and biblical landmarks invite exploration and deeper understanding of the historical and religious context of the Old Testament.
Ancient civilizations of the Bible world
The Old Testament encompasses a rich tapestry of history, populated by numerous ancient civilizations. These civilizations played significant roles in shaping the narratives and events recorded in the sacred scripture. Let’s explore the remarkable biblical cities, ancient locations, and significant sites associated with these civilizations.
Sumerians and Babylonians
One of the earliest civilizations in the Bible world were the Sumerians, who flourished in Mesopotamia. Their renowned cities such as Ur, Nippur, and Eridu are mentioned in biblical accounts. The Babylonians, successors to the Sumerians, notably built the magnificent city of Babylon and the Hanging Gardens, which became symbols of their advanced civilization.
Phoenicians
The Phoenicians, inhabitants of ancient Canaan, were renowned seafarers and traders. Their coastal cities, including Tyre and Sidon, were major centers of commerce and culture. The Phoenicians are remembered in the Old Testament for their contributions to the construction of Solomon’s Temple and their influence on Israelite society.
Syrians and Arameans
The region of Syria was home to several ancient civilizations, including the Syrians and Arameans. These civilizations had great influence throughout the Old Testament period, with cities like Damascus and Hamath playing significant roles in biblical history. The Arameans, in particular, had a lasting impact on the development of the Hebrew language and culture.
Egyptians
Egypt holds a prominent place in the Old Testament, with references to its mighty civilization. The Egyptians are well-known for their grand cities, such as Memphis and Thebes, which feature prominently in biblical narratives. The Exodus of the Israelites from Egypt and the interactions between the Egyptian pharaohs and Hebrew prophets further highlight the historical significance of Egypt in biblical history.

As we delve into the ancient civilizations of the Bible world, we gain a deeper understanding of the cultural, social, and historical contexts in which the Old Testament narratives unfold. Let’s explore further as we unravel the mysteries of these extraordinary civilizations.
The role of Egypt in biblical history
Egypt, with its rich history and cultural heritage, played a significant role in shaping the narrative of the Israelites in the Old Testament. The complex and varied relationship between Egypt and the Israelites is evident throughout biblical history.
One of the notable stories in the Old Testament is the visit of Abraham to Egypt during a famine. Seeking sustenance, Abraham and his wife, Sarah, traveled to Egypt, where their encounter with the pharaoh unfolded.
“Now there was a famine in the land. So Abram went down to Egypt to sojourn there, for the famine was severe in the land. When he was about to enter Egypt, he said to Sarai his wife… And when the princes of Pharaoh saw her, they praised her to Pharaoh. And the woman was taken into Pharaoh’s house.” – Genesis 12:10-15
Another prominent figure in the biblical narrative is Joseph, who rose to power in Egypt as the second-in-command to Pharaoh. Joseph’s story encompasses themes of betrayal, slavery, and eventual triumph, as he became instrumental in saving Egypt and his own family from famine.
“So Joseph went after his brothers and found them at Dothan. They saw him from afar, and before he came near to them, they conspired against him to kill him. They said to one another, ‘Here comes this dreamer. Come now, let us kill him and throw him into one of the pits.’” – Genesis 37:17-20
The Exodus from Egypt is another pivotal event in the Old Testament. Under the leadership of Moses, the Israelites escaped slavery in Egypt and embarked on a journey towards the Promised Land. This significant event solidified the Israelites’ identity as a chosen people and shaped their future.
The mention of Egypt in the Old Testament also extends to the exile of the Israelites. During times of political turmoil and crisis, Egypt served as a place of refuge for the Israelites.
Notable locations in Egypt mentioned in the Old Testament include:
- Goshen – the region where the Israelites dwelled during their time in Egypt.
- The Nile River – an iconic natural feature that played a crucial role in the biblical narrative.
- Memphis – a historic city in ancient Egypt, renowned for its cultural and political significance.
- Thebes – an ancient city that boasted grand temples and was considered the religious center of ancient Egypt.
These locations, along with others, served as backdrops to the stories and events chronicled in the Old Testament, contributing to the rich tapestry of biblical history.

The significance of Canaan (Palestine)
Canaan, also known as Palestine, holds immense significance in the Old Testament. This region was promised to the Israelites as their inheritance and became the land of the twelve tribes of Israel. Many important cities and landmarks are mentioned in the Old Testament, including Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Jericho, Hebron, and the Jordan River. These locations played crucial roles in the narratives of the Old Testament, from the conquest of the Promised Land to the establishment of the Kingdom of Israel.
The city of Jerusalem, often referred to as the “City of David,” is mentioned numerous times in the Old Testament. It served as the capital of the united Kingdom of Israel under King David and his son, King Solomon. Jerusalem was not only a political and administrative center but also a holy city, housing the first temple built by Solomon and later the second temple during the time of the Babylonian exile.
Bethlehem, the birthplace of King David and later Jesus Christ, is another significant biblical city located in Canaan. It holds immense importance in both Jewish and Christian traditions, symbolizing the humble beginnings of the Davidic lineage and the birth of the Messiah.
“But you, Bethlehem Ephrathah, though you are small among the clans of Judah, out of you will come for me one who will be ruler over Israel, whose origins are from of old, from ancient times.” – Micah 5:2 (NIV)
Jericho, known for its famous walls and the miraculous destruction by the Israelites during the conquest of Canaan, stands as a testament to God’s power and faithfulness. This ancient city is mentioned in numerous biblical stories, including the account of Joshua and the battle of Jericho.
Hebron, another prominent city in Canaan, is often associated with Abraham, the patriarch of the Israelites. It was in Hebron that Abraham settled and buried his wife Sarah, along with other ancestors and significant figures mentioned in the Old Testament.
The Jordan River, flowing through the heart of Canaan, holds immense religious and symbolic importance. It served as a natural boundary and was the site of significant biblical events, such as the crossing of the Israelites into the Promised Land under the leadership of Joshua.

These biblical cities, holy sites, and ancient locations in Canaan (Palestine) not only have historical and geographical significance but also serve as important spiritual and cultural landmarks. Exploring these sites helps us better understand the rich tapestry of the Old Testament and the profound impact it has had on the world.
The neighboring regions of the Holy Land
The Holy Land, with its rich biblical history, was surrounded by neighboring regions that played significant roles in shaping the events and narratives of the Old Testament. Two key regions worth exploring are Transjordan and Asia Minor.
Transjordan
To the east of Palestine, Transjordan encompassed the lands of Edom, Moab, and Ammon. These regions had deep historical connections to the Israelites and are mentioned in the Old Testament. Edom, situated south of the Dead Sea, had a rocky relationship with the Israelites, at times serving as adversaries or providing refuge. Moab and Ammon, located east of the Dead Sea, also had interactions with the Israelites, often influenced by alliances or conflicts.
Asia Minor
Asia Minor, known today as modern-day Turkey, was home to various civilizations mentioned in the Old Testament. One notable civilization was the Hittites, who had a significant impact on the biblical world. The Hittites were known for their military and diplomatic prowess and their interactions with both Egypt and biblical Israel. Asia Minor was a region of cultural diversity, with other civilizations such as the Phrygians, Lydians, and others, each leaving their mark on the historical landscape.
“The neighboring regions of the Holy Land provided both allies and adversaries to the Israelites, influencing their interactions and shaping their history.”
Comparative Table – Transjordan and Asia Minor
| Region | Significance |
|---|---|
| Transjordan | Served as both allies and adversaries to the Israelites. Edom, Moab, and Ammon had historical connections and interactions mentioned in the Old Testament. |
| Asia Minor | Home to various civilizations, including the Hittites, who played a significant role in the biblical world. The region was known for its cultural diversity. |

The neighboring regions of the Holy Land added depth and complexity to the narratives of the Old Testament. Exploring the historical places in the Bible, ancient locations, and biblical landmarks in these regions enlightens us about the interconnectedness of the biblical world and the significant role these neighboring regions played in biblical history.
The coastal regions and their significance
The coastal regions of the Bible world played a significant role in biblical history, with Phoenicia and the Philistine cities being of particular importance. Known for their strategic coastal locations, these regions were hubs of cultural exchange, trade, and occasional warfare.
Phoenicia: Renowned Seafarers and Traders
Phoenicia, located along the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea, was home to skilled seafarers and traders. The Phoenicians played a crucial role in the construction of Solomon’s Temple, supplying the materials and expertise needed for its grandeur. Their maritime commerce extended throughout the region, facilitating trade and cultural exchange with neighboring nations.
The Philistine Cities: Conflict and Coexistence
The Philistine cities, including Gaza and Ashkelon, were often in conflict with the Israelites and are prominently mentioned in the Old Testament. These coastal city-states were known for their military prowess and their encounters with the Israelites shaped their shared history. The Philistine cities also served as gateways for both trade and cultural influences flowing between the Mediterranean and the inland regions.
“The Philistines, the leading maritime power of the time, were often at odds with the Israelites, resulting in significant conflicts.” – Book of Judges
The Significance of Coastal Regions
The coastal regions were not only centers of trade and conflict but also places of cultural exchange. Through interactions with seafaring nations, the Israelites were exposed to new ideas, technologies, and beliefs, influencing their own cultural and religious practices. These coastal regions were integral to the narrative of the Old Testament, shaping the destiny of the Israelites and playing a vital role in their historical journey.
The central highlands and their significance
The central highlands, also known as the hill country, were the heartland of the Israelites and the location of several important biblical cities. Cities such as Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Hebron, and Samaria were situated in the central highlands. These cities became centers of religious worship, political power, and historical events. The central highlands also provided natural fortifications and strategic advantages for the Israelites in their struggle for control of the Promised Land.
One of the most significant cities in the central highlands is Jerusalem. Considered holy by multiple religions, it holds immense historical and spiritual importance. Jerusalem is mentioned numerous times throughout the Old Testament and is associated with several key events, including the establishment of King David’s kingdom and the construction of the First and Second Temples.
Bethlehem, another city in the central highlands, is famous for being the birthplace of Jesus. It is mentioned in the Old Testament as the hometown of King David and is closely associated with the Messianic prophecies.
Hebron, located in the southern part of the central highlands, has a rich biblical history. It is mentioned in the Old Testament as a place of significance for the patriarchs Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob. Hebron is specifically associated with the tomb of the patriarchs, which is considered a sacred site by both Jews and Muslims.
Samaria, situated in the northern part of the central highlands, was once the capital of the Kingdom of Israel during the divided monarchy. It played a vital role in the political and religious history of ancient Israel.
Significance of the central highlands:
- The central highlands were the geographic and cultural heartland of the Israelites.
- Important biblical cities such as Jerusalem, Bethlehem, Hebron, and Samaria were located in this region.
- These cities served as centers of religious worship and political power.
- The central highlands provided natural fortifications, making it strategically advantageous for the Israelites.
The central highlands played a vital role in the historical events depicted in the Old Testament. From the establishment of the Davidic dynasty to the birth of Jesus, this region holds immense significance in biblical narratives and continues to be a source of inspiration for millions around the world.
The Jordan River Valley
The Jordan River Valley holds great significance in the narratives of the Old Testament. Flowing through the region, this ancient location is mentioned in various biblical accounts. The cities along the banks of the Jordan River, including Jericho and Bethany, play important roles in the biblical stories.
The Jordan River itself holds symbolic meaning as a representation of crossing into the Promised Land. One of the most iconic events is the crossing of the Jordan River by the Israelites under the leadership of Joshua. This miraculous event marked a pivotal moment in the history of the Israelites as they entered the land promised to them by God.
The Jordan Valley served not only as a natural boundary but also as a route of passage for ancient civilizations. Its strategic position made it a significant location for trade, migration, and military endeavors throughout history. The Jordan River Valley resonates with historical and spiritual significance, making it a sacred spot for those seeking to connect with the ancient biblical narratives.
Conclusion
Throughout the Old Testament, we discover a rich tapestry of Old Testament places that play a pivotal role in the narratives and history preserved in the sacred scriptures. From biblical cities to holy sites, ancient locations to biblical landmarks, these significant sites in the Old Testament hold immense significance in our understanding of the cultural, historical, and religious context of this ancient text.
Exploring these historical places in the Bible allows us to delve deeper into the stories of the Israelites and the neighboring nations, uncovering the mystique of sacred spots and their impact on the unfolding events. From the ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia and Egypt to the coastal regions of Phoenicia and the central highlands of Canaan, we gain a broader perspective on how these Old Testament places shaped the lives of those who walked these lands thousands of years ago.
By studying these ancient locations, we not only gain insights into the past but also gain a deeper appreciation of the Old Testament’s timeless messages and lessons. These biblical cities, holy sites, and biblical landmarks serve as tangible reminders of the faith, struggles, and triumphs of the people of God. They provide us with a glimpse into a world long gone, yet one that still holds relevance and inspiration for millions today.







